통합테스트
요즘은 단위 테스트를 넘어서 통합테스트 / 인수테스트 / E2E테스트를 많이 구성한다.
외부 API를 호출하는 코드가 있다. 해당 로직을 Mocking할 때 어떻게 할 지 생각해보자.
주문 시스템 (예시 코드)
예시를 위해 제작한 주문 시스템의 코드를 보자.
아래는 첫 주문 기능의 진입점인 주문 컨트롤러이다.
@RestController
class OrderController(
private val orderService: OrderService,
) {
@PostMapping("/order")
fun order(
@RequestBody orderRequest: OrderRequest,
): OrderResponse {
orderService.order(orderRequest.userId, orderRequest.productId)
return OrderResponse(isSuccess = true)
}
}아래는 주문 서비스이다. 주문 서비스는 결제 서비스를 호출한다.
@Service
class OrderService(
private val productService: ProductService,
private val paymentService: PaymentService,
) {
fun order(
userId: Long,
productId: Long,
) {
val product = productService.get(productId)
productService.verify(product)
val paymentResult = paymentService.payment(userId, product.amount)
if (!paymentResult.isSuccess) {
throw PaymentException("주문이 실패했습니다.")
}
// 주문 로직
println("주문 완료!")
}
}아래는 결제 서비스이고, 외부 API를 호출한다.
@Service
class PaymentService(
private val paymentApiClient: PaymentApiClient,
) {
fun payment(
userId: Long,
amount: Amount,
): PaymentResult {
val request = PaymentRequest(userId, amount)
return paymentApiClient.payment(request)
}
}테스트 코드
테스트 코드는 아래와 같다. 통합 테스트를 할 때 MockMvc, RestAssured, Cucumber 등 다양한 도구를 사용할 수도 있다.
아래에서는 RestAssured를 사용해서 인수 테스트를 구성했다.
class OrderAcceptanceTest : BaseAcceptanceTest() {
@Test
@DisplayName("사용자는 상품을 주문할 수 있다.")
fun order() {
val response = 뿌링클을_주문한다()
val 응답_데이터 = 주문_응답(response)
assertThat(응답_데이터.isSuccess).isEqualTo(true)
}
fun 뿌링클을_주문한다(): ExtractableResponse<Response> = invokePost("/order", 뿌링클_1마리_주문_요청())
fun 주문_응답(response: ExtractableResponse<Response>) = response.`as`(OrderResponse::class.java)
}
fun 뿌링클_1마리_주문_요청(): OrderRequest = OrderRequest(testUserId, 1L)해당 테스트 클래스가 상속하는 BaseAcceptanceTest는 다음과 같다.
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension::class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class BaseAcceptanceTest {
@LocalServerPort
val port: Int? = null
@MockBean
lateinit var paymentApiClient: PaymentApiClient
@BeforeEach
fun setup() {
RestAssured.port = port!!
given(paymentApiClient.payment(any(PaymentRequest::class.java)))
.willReturn(PaymentResult(true))
}
}
일반적으로 위 코드처럼 외부 API를 Mocking할 때 Service/Adaptor를 모킹하는 경우가 많다. 그런데 한 가지 의문점이 든다.
'이게 필요한 커버리지를 정말 보장하는 테스트 코드인가..?'
테스트 커버리지가 100%라도 안전하지 못할 수 있는 이유도 여기서 나온다.
Web Layer
Web 영역이라고 하면 아래 영역을 포함한다.
- Request를 직렬화
- Response를 역직렬화
- 네트워크 통신
하지만 저런 방식으로 Mocking 하면 세가지 영역 중 어느것도 커버되지 않는다.
Product 코드에는 아래 설정이 존재한다.
@Configuration
class ObjectMapperConfig {
@Bean
fun objectMapper(): ObjectMapper = ObjectMapper()
}ObjectMapper의 Naming 전략은 현재 CamelCase이다. 즉, 외부 API와 통신도 CamelCase로 통신을 한다.
ObjectMapper의 Naming 전략을 변경해보자.
@Configuration
class ObjectMapperConfig {
@Bean
fun objectMapper(): ObjectMapper =
ObjectMapper()
.setPropertyNamingStrategy(PropertyNamingStrategies.SNAKE_CASE)
}이제 ObjectMapper가 통신할 때 SnakeCase로 통신한다. PaymentApi는 CamelCase를 사용하고 있으므로 테스트가 깨져야 정상이다.

하지만 테스트는 정상적으로 통과한다.
ApiAdaptor를 Mocking 하면서 테스트 단계에서 더 이상 직렬화 / 비직렬화가 진행되지 않았고, 해당 영역에 대한 결함을 테스트 코드로 잡을 수 없게 되었기 때문이다. (거짓 음성)
WireMock
WireMock을 사용하면 특정 빈을 모킹하지 않고도 테스트할 수 있도록 Stub Server를 제공한다.
즉, 실제로 직렬화/역직렬화, 네트워크 요청까지도 테스트에 커버할 수 있다는 말이다.
WireMock은 Spring Cloud에서도 스프링 환경에서 WireMock 사용을 위해 라이브러리를 지원하고 있다.
먼저 해당 라이브러리의 의존성을 추가한다.
implementation("org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-contract-wiremock:4.1.3")프로퍼티 설정에서 API 호출 url을 아래와 같이 세팅한다.
apis:
payment:
url: localhost:${wiremock.server.port}Spring Cloud Contract WireMock은 Stub 서버의 포트를 wiremock.server.port 에 바운드한다.
이후 외부 API( /payment)를 호출했을 때 응답을 아래 폴더에 정의한다. 예시의 경우 test/resources/__files/payload/payment-response.json에 정의한다.
{
"success": true
}아래에서 Mocking 서버를 설정하는 메서드를 정의한다.
class WireMockContext {
companion object {
fun setupPaymentApi() {
stubFor(
WireMock
.post(WireMock.urlMatching("/payment"))
.willReturn(
WireMock
.aResponse()
.withStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value())
.withHeader("Content-Type", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
.withBodyFile("payload/payment-response.json"),
),
)
}
}
}이제 PaymentApiClient를 Mocking하는 부분을 없애고 해당 메서드를 호출하기만 하면 된다.
@AutoConfigureWireMock(port = 0)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class BaseAcceptanceV2Test {
@LocalServerPort
val port: Int? = null
@BeforeEach
fun setup() {
RestAssured.port = port!!
WireMockContext.setupPaymentApi()
}
}이제 실제로 테스트를 실행해보면 PaymentApiClient를 실제로 호출해서 요청을 한다. 그래서 직렬화 전략이 SnakeCase일 경우 아래와 같이 테스트가 실패한다.
isSuccess 필드가 역직렬화에 실패해서 기본 값인 false가 들어가 테스트가 실패한 것이다.
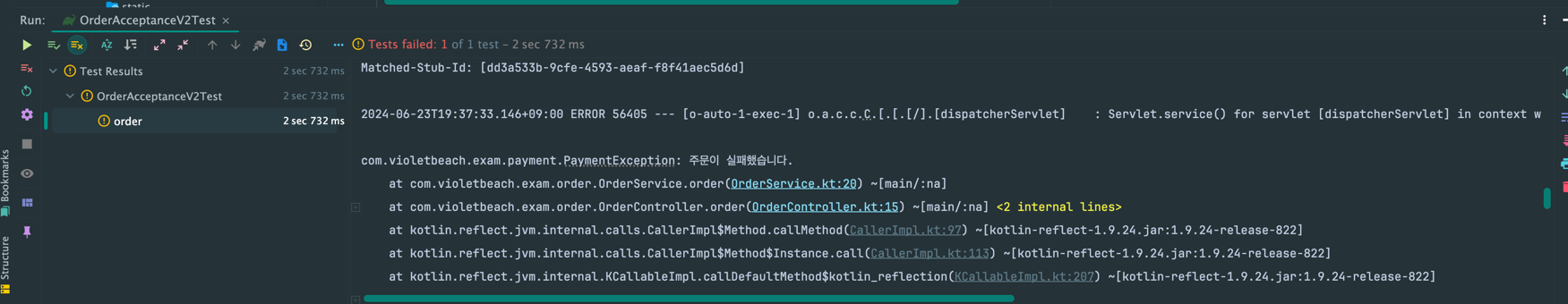
WireMock을 사용함으로써 직렬화 / 역직렬화 및 네트워크 통신에서의 문제도 잡을 수 있게 된 것이다.
번외 - 통합 테스트의 범위
위에서 말한 것은 통합테스트의 범위에 따라 다르다. 만약 직렬화/역직렬화 및 네트워크 통신을 포함한 범위를 테스트 하고자 한다면 WireMock을 사용해서 서버 자체를 Stub 하는 방식이 좋다.
추가로 고려해야 할 점은 해당 프로젝트 자체의 Input/Output도 고려해야 한다는 점이다.
class OrderAcceptanceTest : BaseAcceptanceTest() {
@Test
@DisplayName("사용자는 상품을 주문할 수 있다.")
fun order() {
val response = 뿌링클을_주문한다()
val 응답_데이터 = 주문_응답(response)
assertThat(응답_데이터.isSuccess).isEqualTo(true)
}
fun 뿌링클을_주문한다(): ExtractableResponse<Response> = invokePost("/order", 뿌링클_1마리_주문_요청())
fun 주문_응답(response: ExtractableResponse<Response>) = response.`as`(OrderResponse::class.java)
}
fun 뿌링클_1마리_주문_요청(): OrderRequest = OrderRequest(testUserId, 1L)해당 테스트는 Input, Output 모두 특정 Object를 사용하고 있고, 직렬화/역직렬화는 빈으로 정의된 ObjectMapper를 따를 것이다.
만약 ObjectMapper의 Case 전략이 바뀐다면 Product/Test 환경 모두 전략이 일치할테니 버그를 잡을 수 없고, 실제로 클라이언트나 외부 시스템에서 호출할 때는 실패할 것임에도 테스트는 성공할 것이다.
class OrderAcceptanceV2Test : BaseAcceptanceV2Test() {
@Test
fun order() {
val response = 뿌링클을_주문한다()
val 응답_데이터 = response.`as`(Map::class.java)
assertThat(응답_데이터.get("is_success")).isEqualTo(true)
}
fun 뿌링클을_주문한다(): ExtractableResponse<Response> = invokePost("/order", 뿌링클_1마리_주문_요청())
fun 뿌링클_1마리_주문_요청() {
val map = HashMap<String, Any>()
map.put("user_id", testUserId)
map.put("product_id", 1)
}
}그래서 인수 테스트를 할 때는 Map 등을 사용해서 Input, Output을 통신하는 데이터 그대로 사용하는 것이 더 안전한 테스트가 된다.
- ATDD를 할 때 별도의 프로덕트 코드 없이 테스트를 먼저 작성할 때도 큰 도움이 된다.
Reference
'Server > JUnit, Spock' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Reactive Streams를 테스트하는 방법 (reactor-test 라이브러리) (0) | 2024.05.04 |
|---|---|
| FixtureMonkey 적용 검토해보기! (0) | 2024.03.23 |
| Unit Test - 리팩토링 내성이란 무엇인가?! (0) | 2023.08.06 |
| ATDD 이해해보기! (0) | 2023.05.17 |
| JUnit - Private method 테스트하기! (feat. Kent Beck) (0) | 2022.11.05 |